
What is Hair Porosity
Hair porosity is your hair’s ability to absorb and maintain moisture. The porosity level of your hair is therefore responsible for how well oil and moisture can absorb or expel from the outer layer of your hair.
Hair is naturally porous and absorbs moisture. Hair can have high, medium, and low porosity. This varies with the type of hair, age of the hair, length of the hair, the chemicals used on the hair and the condition and shape of hair. On a head of hair, it can have all types: low, medium and high. Natural curly or coily textured hair tends to be more on the porous side than Asian and Caucasian hair.
Low Porosity Hair
The cuticles are tightly packed and lay flat. As a result, it is more resistant to water, hair products and chemical treatments. The hair takes longer to wet and dry. Products build up on the hair and therefore don’t absorb well. Protein treatments make the hair feel stiff and chemical treatments aren’t as effective and don’t perform as they should.
Medium Porosity Hair
The cuticle layer is looser, as a result, can allow moisture to absorb and maintain moisture. The hair can retain water and hair products well. Chemical treatments respond on the hair and perform as they should. This hair requires the least amount of maintenance.
High Porosity Hair
Cuticles are more widely spaced, therefore allowing for the absorption of water and hair products quickly. But, this type of hair, however, can allow moisture to also escape, leaving it dry. For example, this can cause breakage and frizzy hair. Chemical treatments also reacts quickly on the hair and don’t perform how they should. In addition hair can have high porosity due to damage from heat styling, perms, coloring, relaxing, rough combing and the environment. Textured hair is more susceptible because the cuticle can lift up the hair strands at the twists for curly, kinky and coily hair.
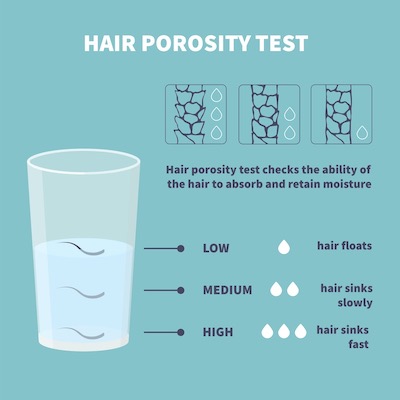
Porosity Test
These are ways to test the porosity of your hair.
Spray Test
Spray hair with water on clean dry hair. Low porosity hair takes longer to absorb the water, the water beads up on the hair. The hair takes longer to dry. Medium porosity hair absorbs the water and retains the water. The hair dries not too fast and not too slow. High porosity hair absorbs the water quickly and dries quickly.
Float Test
Place a few clean hair strands into room temperature water. After a few minutes, if the hair floats it is low porosity. If the hair sinks quickly, it is high.
Formulating for Hair Porosity
Low Porosity
These hair products should contain moisturizers, rich emollients, and humectants. These ingredients add moisture to the hair. Use hydrating mist, serums, leave-in conditioner, deep conditioner or mask. Use a steamer to enhance penetration of conditioning treatments. Minimize or don’t use butters on the hair.
Medium Porosity
A deep conditioner with protein can be occasionally used.
High Porosity
Most importantly, these hair products should contain anti-humectants. Conditioning products need to be used to smooth the hair. Use hydrating mist, hair oil, leave-in conditioner, hair cream and protein treatments. Try oils like avocado oil, baobab oil, passion fruit oil and small amount of plant butter. These hair care products can also help seal the hair from losing moisture in hot or humid climates.
The Science of Hair
In conclusion, now that you understand a bit more about hair, you can continue to learn about the science of hair. Check-out our posts on Hair Shape and Hair Anatomy. To formulate exceptional hair care products, it is important to have an understanding of the science of hair.
In addition, we also teach all about Hair Science in our Diploma Pro Natural Hair Care Formulation Course. Become a Natural Hair Care Expert and Formulator and Start a Self-Study Course today!
Hair Science Lesson includes:
- Hair Anatomy
- Hair Structure
- Hair Density
- Hair Texture
- Hair Porosity
- Hair Shape
- Hair Types
- Curl Pattern
You might also like

